High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Treatment
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion treatment. Its hybrid morphology poses a pathologic challenge. 3 linhas If high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion cytology or a high-grade colposcopic. A young age 25 years and pregnancy are two factors associated with higher regression rates of untreated high-grade abnormalities.
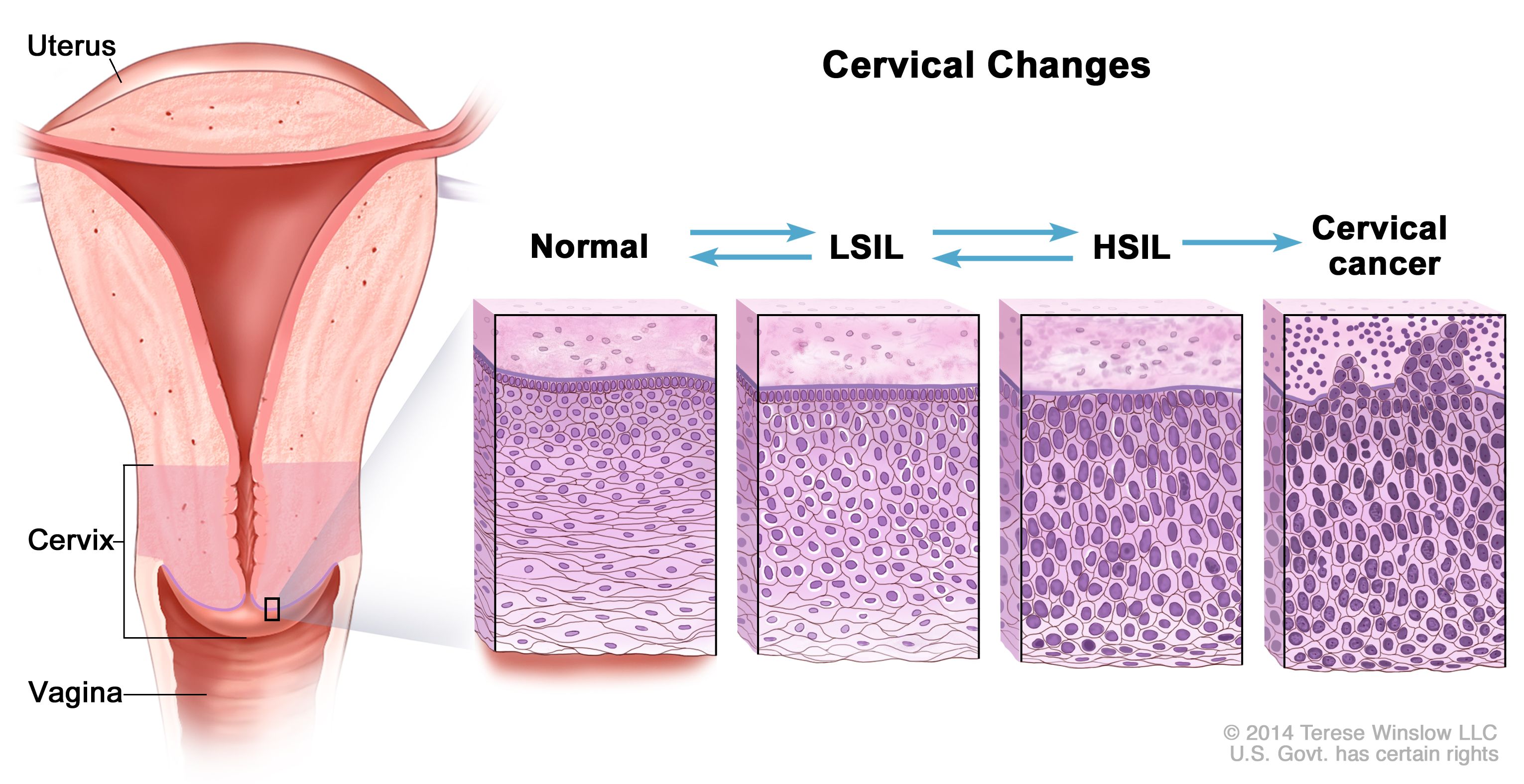
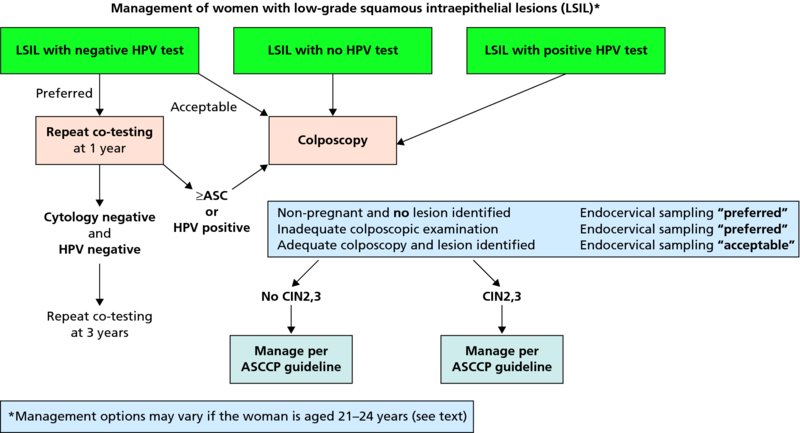
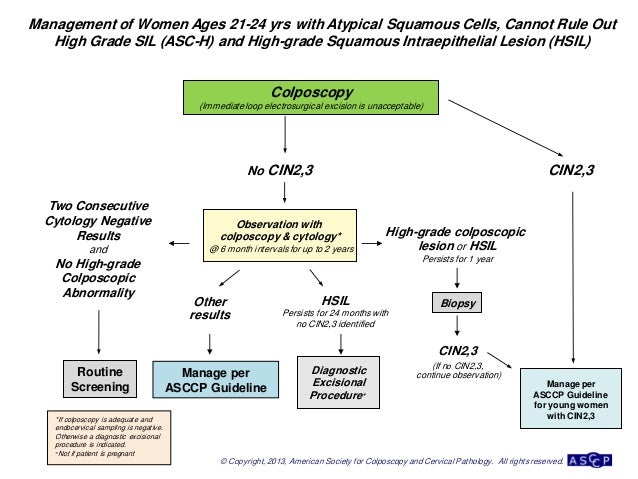
HSIL is caused by a virus called human papillomavirus HPV that infects the cells in the vagina. Ablative treatment destroys the abnormal tissue. A high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion is noted with pap next management includes a Warthims hysterectomy b Local excision c Colposcolic study and biopsy d HPV DNA testing e Liquid based cytology Correct Answer - C Ans iscie Colposcolic study and biopsy For high grade intraepithelial lesions HSIL first step is to do colposcopy and biopsy.
Objectives Stratified mucin producing intraepithelial lesion SMILE is an uncommon premalignant cervical intraepithelial lesion characterized by histopathologic features resembling those observed in high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and adenocarcinoma in situ of the cervix. The colposcopically directed LEEP after a HGSIL on PAP-smear may reduce the time interval between diagnosis and treatment with a similar accuracy of diagnosis compared to. Current therapies for HSIL and anal cancer are highly invasive.
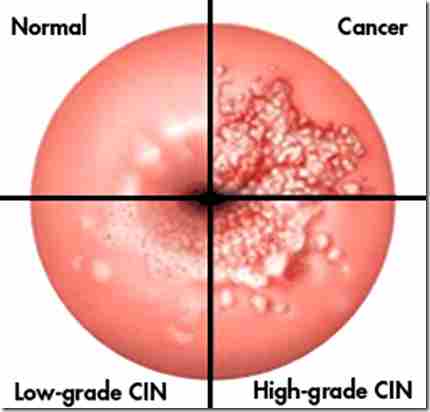
Ablative treatment is another possible treatment your doctor may recommend. Excisional Treatment for Low Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Conization. Whether the lesion is high grade or low grade is determined by taking a tiny biopsy of the lesion.
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion may eventually lead to invasive cancer of the cervix when managements are not instituted. Most common techniques used. Cranston RD Baker JR Liu Y et al.
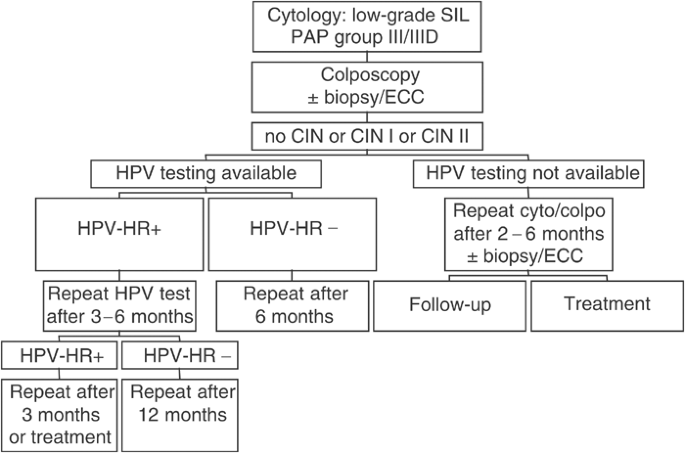
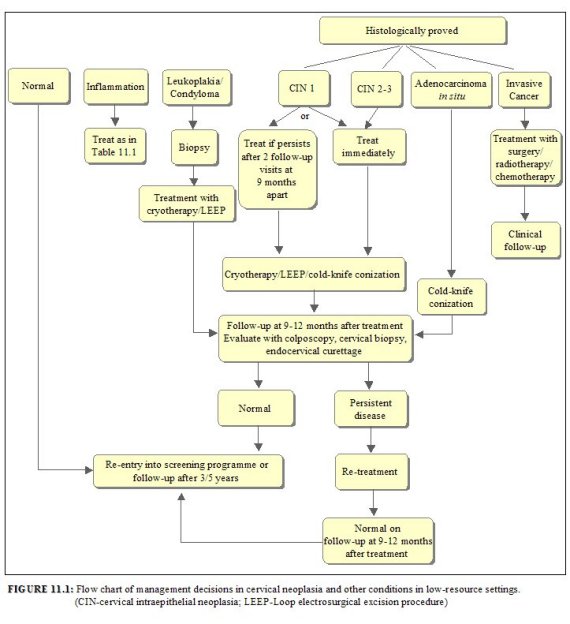
Current recommendations for management of high-grade lesions the efficacy of treatment options cryotherapy and LEEP and the immediate bleeding infection and longer term complications cervical incompetence preterm delivery of cervical dysplasia treatment are presented. Some lesions especially LSIL spontaneously resolve on their own without treatment. Treatment options for high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion As expected methods for addressing HSILs are different from LSILs.
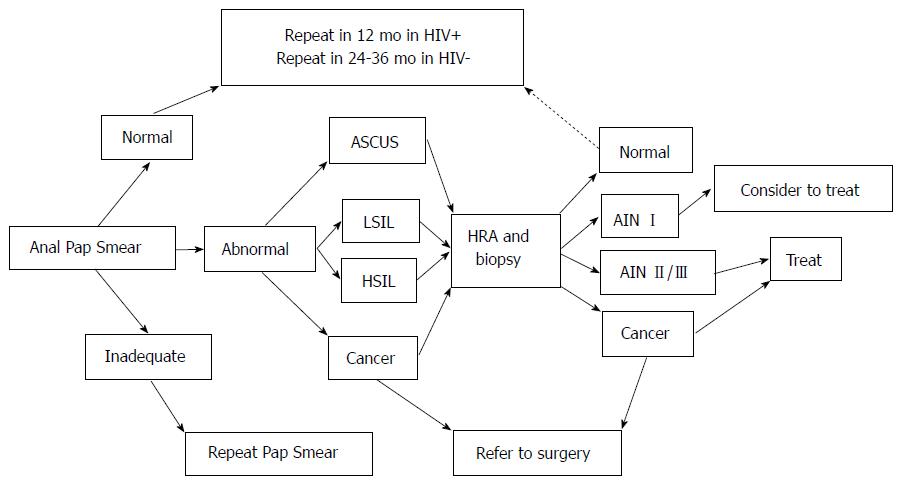
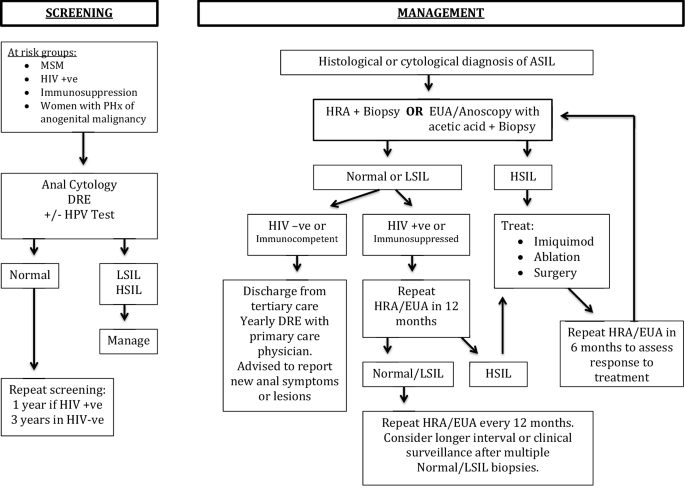
Currently ACOG guidelines advise performing a colposcopy and potential excision of intraepithelial lesions. Lesions are generally found by a clinician using HRA high resolution anoscopy.
HSIL is caused by a virus called human papillomavirus HPV that infects the cells in the vagina.
A see and treat versus a three-step approach. Its hybrid morphology poses a pathologic challenge. High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion HSIL is a pre-cancerous disease that develops in the vagina. Treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Being carcinoma in situ it is considered stage 0 cervical cancer but may not indicate that there is already cervical cancer. The presence of HSIL should be treated to prevent the development into cervical cancer. Ablative Treatment In ablative treatment the abnormal cells are removed from the cervix. Ablative treatment destroys the abnormal tissue. 3 linhas If high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion cytology or a high-grade colposcopic.
Treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. HSIL is caused by a virus called human papillomavirus HPV that infects the cells in the vagina. Cranston RD Baker JR Liu Y et al. Sex Transm Dis 2014. It can be done in two ways. The colposcopically directed LEEP after a HGSIL on PAP-smear may reduce the time interval between diagnosis and treatment with a similar accuracy of diagnosis compared to. It is known that prior to development of anal cancer a person develops a precancerous condition known as a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion HSIL.






























Posting Komentar untuk "High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion Treatment"